Key Takeaways 🔥
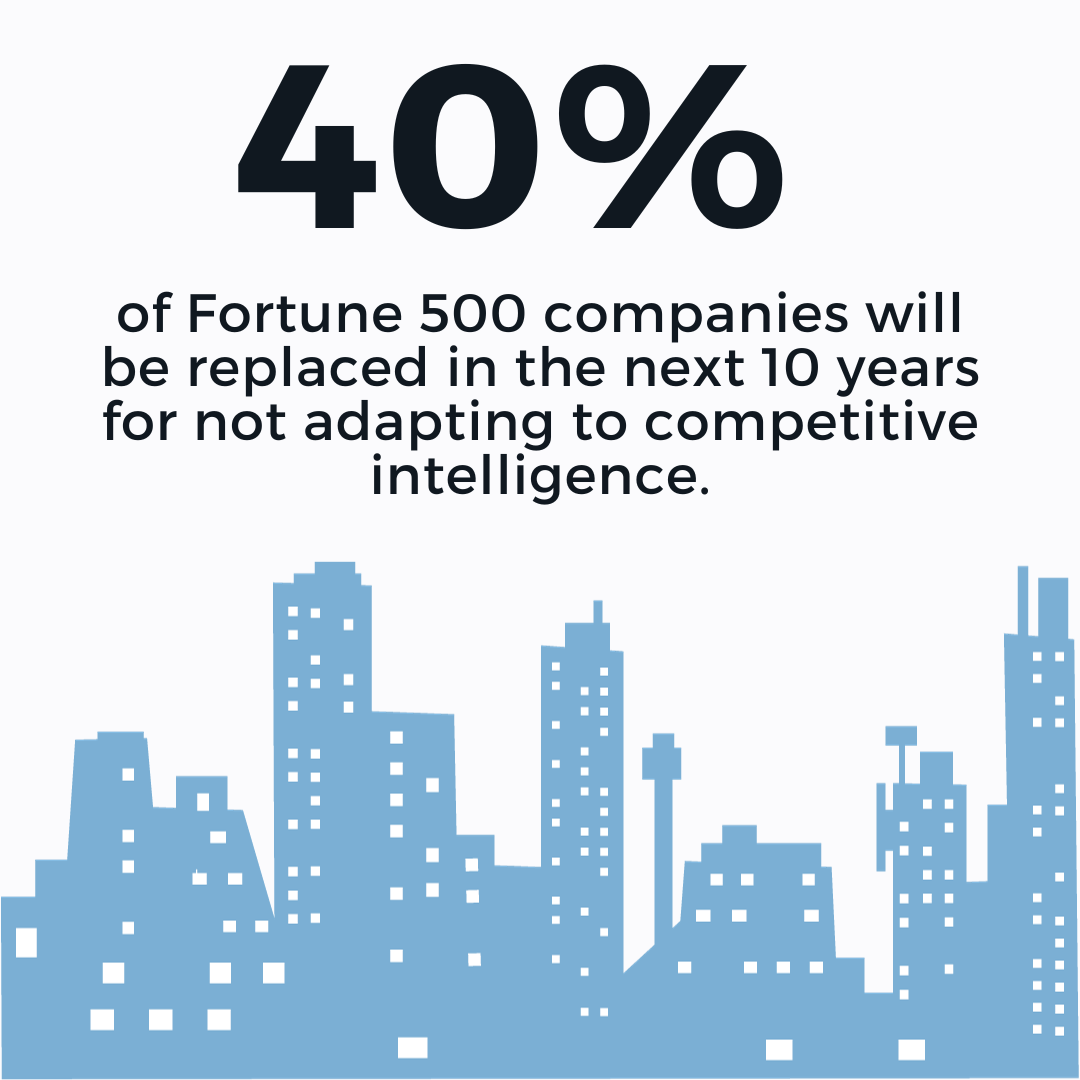
- Competitive Intelligence is Essential Today: Competitive intelligence (CI) research ethically gathers and analyzes data about a company’s competitive environment, including competitor activities and market trends. Understanding these external forces is crucial for strategic decision-making in the current fast-paced business landscape.
- CI Drives Marketing Strategy: Competitive intelligence plays a significant role in marketing research. By understanding competitor offerings and customer perceptions, marketing teams can craft value propositions that resonate with customers and differentiate from competitors.
- Evolution of CI Research: CI research has evolved significantly since the 1980s. From collecting print publications to leveraging the internet, digital data, and advanced analytics, the scope and scale of CI have expanded, making it more sophisticated and actionable.
- Emergence of New CI Technologies: Modern competitive intelligence methodologies have been transformed by new technologies. Tools like web scraping, API-based tracking, and advanced analytics allow real-time monitoring and predictive analysis of competitor actions.
- Key Areas of CI Research: The primary focus areas of CI research include Market Intelligence, Competitor Intelligence, M&A Intelligence, and Win/Loss Analysis. These areas provide the knowledge required to drive strategy and outperform rivals.
- Emerging Trends in CI: Significant trends shaping CI research include Big Data and Advanced Analytics, Automation, Social Media Monitoring, and Cyber Intelligence. These trends enhance the comprehensiveness and actionability of CI.
- Importance of Integrating CI: Companies should integrate competitive intelligence into their core decision-making processes for maximum impact. This involves regular strategy meetings, cross-functional CI teams, and training employees to apply CI insights effectively.
Definition of Competitive Intelligence Research
Competitive intelligence (CI) research ethically and legally collects and analyzes information about a company’s competitive environment. This includes monitoring competitor activities, strategies, and offerings and analyzing broader market forces, trends, and opportunities. While companies have long used competitive intelligence, its importance in today’s global and rapidly evolving business landscape cannot be overstated.
With everything from technology disruptions to shifting consumer behaviors challenging traditional business models, executives must keenly understand the external competitive forces impacting their organizations. Competitive intelligence provides the insights needed to make strategic decisions about entering new markets, responding to competitor moves, introducing new products or services, setting prices, and preparing for potential acquisitions or partnerships.
62% of companies plan to increase spending on competitive intelligence in the future (Source: State of Competitive Intelligence)
Leaders today rely on competitive intelligence to identify threats, remain agile, capitalize on trends, and make their companies more resilient to market volatility. Effective CI is mission-critical, directly influencing a company’s ability to gain and maintain competitive advantage.
What’s the Data Say About Competitive Intelligence?
Competitive intelligence and data analytics have become indispensable strategic tools for enterprises seeking a competitive edge. An overwhelming 90% of Fortune 500 companies already utilize competitive intelligence, with 94% of all businesses planning investment in this area. Data-driven insights allow 74% of firms to differentiate strengths for stakeholders, making decision-making 5x faster.
Looking ahead, most organizations see gaining advantage as a top priority. 57% rank it among their top 3 goals, while 53% of CEOs express concern over disruptive competition. To stay ahead, 73% allocate over 20% of their tech budgets to research and analytics.
Leveraging these tools, 56% of executives monitor potential competitors, devising plans to conquer new markets in the next three years. With widespread adoption among global leaders, competitive intelligence and advanced analytics appear essential to outmaneuvering rivals in today’s cutthroat business landscape.
Competitive Intelligence in Marketing Research
Competitive intelligence plays a pivotal role in marketing research and strategic planning. By thoroughly understanding competitor offerings, positioning, messaging, channels, and customer perception, marketing teams can identify vulnerabilities to exploit and strengths to emulate or avoid.
Ongoing competitor intelligence enables marketers to assess promotional campaigns, product launches, pricing changes, and brand messaging through a strategic lens. They can determine potential impacts on market share and growth opportunities. Marketing leverages CI to craft differentiated value propositions and messaging that resonate with customers relative to competitors.
CI also informs marketing mix optimization and budget allocation decisions based on competitor spend and channel presence. CI provides early warning signs of how competitors react when launching new products. Across strategic, tactical, and operational marketing activities, competitive intelligence provides the external context and insights needed to make decisions that maximize opportunities and competitive advantage.
Marketing cannot rely on internal data alone – competitor intelligence must inform strategies and planning. Combining holistic CI with marketing analytics provides a powerful fact base to enhance marketing programs’ agility, accuracy, and effectiveness in competitive contexts. With CI input, marketing teams can look forward instead of just looking back when driving critical initiatives.
The Evolution of Competitive Intelligence Research
A Brief History of How CI Research Has Evolved
Competitive intelligence as a formal practice became prominent in the 1980s as companies realized the strategic value of studying their competitors and industry trends. In the early days, CI focused on collecting print publications, news clips, and other manual information sources to gather intelligence.
By the 1990s, the internet, digital information, and new data mining technologies opened up immense possibilities for tech-enabled competitive research. Companies assembled intelligence groups to scour the web, databases, forums, and early social networks to find everything they could on competitors. This ushered in an era of expanding the scope and scale of CI via new digital sources.
The 2000s saw further advances as CI software systems emerged to automate intelligence gathering and analysis. CRM and market research data also provided insights into customers that bolstered competitive knowledge. CI grew more centralized in companies, with dedicated analysts and data scientists deriving powerful insights from all the information readily available digitally.
Today, competitive intelligence leverages advanced analytics, big data, AI, and specialized tools to continuously track and make sense of competitor information across countless sources. Social media monitoring, online listening platforms, and automated web scrapers feed volumes of fresh data to analysts. Data science enhances the sophistication of analysis to reveal what competitors are doing and predict what they may do.
New Technologies & Data Sources Emerge
Today’s competitive intelligence methodologies, tools, and outputs would have been unfathomable 20 years ago. CI has been completely transformed by new technologies that enable more powerful gathering and analysis of intelligence.
Firstly, the proliferation of digital information sources means more data to leverage about competitors. Analysts can incorporate signals from company websites, digital marketing content, social platforms, app store reviews, GitHub repositories, domain registrations, resume databases, and unlimited other sources—this data diversity fuels analysis breadth and depth.
Powerful web scraping and API-based tracking tools can automatically collect competitor data at scale and feed it into centralized intelligence systems. This enables near real-time monitoring of digital signals. Automated alerts can flag relevant updates for analysts to hone in on. No longer is manual searching through individual sources required.
Growth opportunities and competitive pressures drive companies to pursue digital transformation. 51% of firms say new growth prospects fuel their digital evolution, while 41% point to intensifying competitive threats in their market. Together, these outward market forces motivate over 90% of digital transformation initiatives as companies seek to capitalize on new possibilities and keep pace with rivals (Source: Prophet)
Sophisticated analysis software helps uncover hidden relationships and patterns in the expansive data. It provides visualization dashboards to help make sense of competitor ecosystems. Natural language processing assists with analyzing unstructured text data. Predictive modeling and simulation anticipate competitor behavior. Advanced analytics turn information overload into strategic foresight.
Competitive intelligence analysts’ productivity and strategic capabilities have grown tremendously thanks to these technology enablers. While CI remains focused on informing business strategy, the processes, scale, and sophistication attained demonstrate how far this function has progressed in just decades—the advent of artificial intelligence promises to unlock even more potential in the future.
Key Focus Areas: Competitive Intelligence Research
| Area of Focus | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Intelligence | Analyzing competitors, customers, suppliers, partners, and market forces to understand industry dynamics and support strategic decisions. |
| Competitor Intelligence | Monitoring competitor activities, offerings, strategies, and performance to detect opportunities and threats. |
| M&A Intelligence | Researching potential acquisition targets by assessing product portfolios, IP, revenues, valuations, culture fit and synergies. |
| Win/Loss Analysis | Determining factors influencing winning and losing deals, such as pricing, product features, messaging, and buyer criteria. |
Market intelligence – Analyzing Competitors, Customers, and Suppliers
A key focus area is developing market intelligence by thoroughly profiling and assessing companies in the competitive ecosystem. This provides insights into competitors’ product offerings, positioning, strengths vs. weaknesses, corporate strategy, and areas primed for disruption. Deep market analysis might examine customer segments, pricing, distribution channels, partnerships, hiring trends, patents, and M&A activity. Developing these intelligence perspectives on the market fuels strategic planning.
Comprehensive market intelligence provides the competitive clarity needed to thrive. Organizations gain essential visibility into product landscapes, value propositions, capability gaps, corporate priorities, and vulnerabilities by thoroughly analyzing competitors, customers, suppliers, startups, and partners. This enables data-driven strategy and planning to capitalize on growth opportunities and disrupt rather than be disrupted. With markets constantly evolving, ongoing collection and synthesis of intelligence on ecosystem players provides the context critical for strategic agility and competitive resilience. Companies that fail to prioritize rich market intelligence risk misjudging threats, missing trends, and formulating flawed strategies.
Competitor Intelligence – Monitoring Competitor Activities and Strategies
Ongoing competitor intelligence is vital for staying on top of rival companies’ latest moves and decisions. This area monitors competitor product launches, marketing campaigns, executive changes, financial performance shifts, patent filings, job postings, acquisitions, geographic expansion, and strategic pivots. This intelligence aids firms in reacting quickly to competitive activity and plotting countermoves.
Comprehensive monitoring provides the insights businesses need to keep pace with competitors. Organizations can build a detailed profile of competitor dynamics by tracking product releases, campaigns, leadership changes, finances, patents, hiring, M&A, global presence, and strategy adjustments. They gain the visibility to respond to market-altering moves and maintain their competitive stance rapidly. With so much on the line, mature competitor intelligence is no longer optional but essential to competing and winning in the modern business landscape. Companies that fail to prioritize monitoring threats and opportunities from rivals risk being blindsided by market events and ceding ground.
Mergers & Acquisitions – Researching Potential Acquisition Targets
M&A-focused intelligence analyzes market spaces and companies to identify promising acquisition targets. This involves assessing target companies’ product portfolios, IP assets, revenues, customer bases, market valuation, key personnel, culture, and business models to determine fit and evaluate risks. Deep research builds understanding to inform acquisition decisions.
Thorough intelligence gathering on potential acquisitions provides insights for strategic inorganic growth. Businesses can fully evaluate suitability, synergies, risks, and valuation by researching targets’ offerings, intellectual property, financials, customers, value, leadership, organizational attributes, and strategies. This level of analysis is essential for making informed M&A decisions and avoiding costly missteps. With so many acquisitions failing to achieve expected returns, rigorous research and intelligence work are crucial. It enables organizations to successfully identify and vet acquisition targets that align with corporate strategy and demonstrate growth potential. This empowers companies to execute deals that enhance competitiveness.
Win/loss Analysis – Determining the Outcome of Deals
Win/loss intelligence examines why sales deals are won or lost to competitors. This looks at product features, pricing, sales messaging, competitive products, purchasing criteria, and buyer sentiment. Intelligence can guide sales enablement and product development to improve win rates.
Detailed win/loss analysis provides actionable insights for gaining competitive advantage. Organizations gain clarity into strengths, weaknesses, and gaps by investigating product attributes, pricing models, sales positioning, rival offerings, customer priorities, and buyer perceptions. Leaders can leverage these intelligence insights to enhance sales targeting, craft differentiated value propositions, optimize pricing, and inform product roadmaps. This enables data-driven improvements that boost win rates. In today’s crowded markets, win/loss intelligence is essential for maximizing competitive performance. Companies that fail to learn from wins and losses risk compromised enablement, misaligned products, and declining win rates.
Emerging Trends Shaping Competitive Intelligence Research
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Big Data & Advanced Analytics | Combining massive, diverse datasets and applying predictive modeling, machine learning, and other techniques to derive deeper insights about competitors and markets. |
| Automation | Leveraging web scraping, APIs, bots, and AI to automate repetitive intelligence gathering and analysis tasks so analysts can focus on higher value work. |
| Social Media Monitoring | Tapping into real-time competitor insights from social platforms and analyzing sentiment, engagement, trends, and perceptions. |
| Cyber Intelligence | Monitoring hacker communications and threats to protect IP and strategic assets from leaks and security breaches. |
Big Data & Advanced Analytics
The explosion of big data and new analytics capabilities dramatically influences competitive intelligence. More profound insights can be derived about competitors by combining massive structured and unstructured datasets, predictive modeling, machine learning, and other advanced techniques.
Big data analytics enhances strategic planning with scenario modeling to determine competitive responses. It enables churn prediction to evaluate customer loyalty vulnerabilities vs. rivals. Powerful text analytics can structurally process social media, reviews, and competitor publications for sentiment, themes, and hidden relationships. Big data transforms reactive tactical monitoring into predictive strategic analysis.
New visual data discovery tools empower analysts to explore findings and draw connections interactively. Dashboards condense voluminous data into dynamic views that focus on critical competitive intelligence. Analytics enhances the value extracted from growing data volumes, enabling nuanced market assessments.
Automation of Intelligence Gathering
The automation of core intelligence activities is freeing up analysts to focus on higher-value analysis. Web scraping tools can programmatically harvest vast amounts of content from competitor websites. APIs and trackers gather near real-time digital signals to feed intelligence systems. Rules-based alerts automatically flag important changes.
Natural language generation turns data into initial written briefs. Email digests summarize daily findings so analysts can quickly absorb updates. Chatbots handle basic competitive questions from internal stakeholders. The goal is to automate repetitive tasks so analysts can specialize in interpretation, strategy assessment, and briefing leadership.
Social Media Monitoring
Given its wealth of real-time insights, social media is a growing competitive intelligence data source. Through monitoring competitor’s social media, analysts can pick up on new hires, product launches, campaigns, events, geographic expansions, and other insights much faster than traditional monitoring.
Sentiment analysis of social content is valuable for assessing consumer perceptions of competitors. Tracking follower growth and engagement benchmarks performance. Competitor social profiles offer a view into company culture and brand personality. The sheer volume requires automation, but social media AI and analytics unlock tremendous competitive knowledge.
Cyber Intelligence & Protecting IP
Cybersecurity threats have made cyber intelligence critical for protecting IP and strategic data. Monitoring hacker forums, dark web sites, and threat actor communications provides warning of possible attacks and leaks. Competitive cyber intelligence aims to preemptively detect and prevent the loss of sensitive internal information.
Firms monitor for IP leaks, enforce cybersecurity best practices, and use technologies like digital rights management to control the use and distribution of strategic assets. With cybercrime threatening confidentiality, cyber intelligence is essential.
Why Competitive Intelligence Research Matters More Than Ever
Research indicates that companies that use intelligence platforms to track prospects and customers generate four times more revenue on average than those that do not. By leveraging technology to gain greater customer insight and monitor progress, firms can boost revenue significantly. The data highlights the substantial financial benefits enterprises can realize by dedicating resources to intelligence gathering and analysis around their pipeline and customers. With sizeable revenue gains verified, investment in robust intelligence platforms is a smart strategic decision for any organization seeking to accelerate growth (Source: Evalueserve Survey)
Velocity of Change Makes Intelligence More Vital
The quickening pace of change across industries and markets means real-time monitoring and insight are imperative. New competitors can seemingly emerge overnight thanks to low barriers to entry. Trends like mobile, AI, and project-based work reshape how and where business is done.
Continuous intelligence reduces disruptive surprise and uncertainty by tracking changes as they occur. This vigilance allows companies to formulate agile responses rooted in understanding rather than just reacting. Intelligent adaptation leads to more robust competitive positioning than playing catch-up after the fact.
Globalization Has Increased Competition
Globalization has intensified competition by removing geographical barriers to entry. Any company must now consider rivals from all corners of the world, not just domestically. This makes broad competitive monitoring essential. Companies must assess global competitors holistically while valuing vital regional differences in offerings, strategy, and local partnerships.
Disruption from New Technologies and Business Models
Disruptive innovation frequently upends once-stable markets. Forward-looking intelligence analysis of emerging technologies can reveal opportunities and threats earlier. Monitoring technology trends and startups helps incumbents consider if pre-emptive adoption, acquisition, or adaptation is warranted. Deeper technology intelligence also informs new R&D and product roadmaps.
New data-centric business models also compel intelligence programs to incorporate non-traditional signals. Web scrapers, analytics, and social data provide valuable clues to online competitive moves. Intelligence must rapidly evolve along with the forces driving disruption.
The Need for Data-Driven Strategic Decisions
With competitive pressures mounting, leaders cannot afford to make intuitivist strategic calls. Data-driven intelligence provides the evidence for critical moves like entering new geographies, acquiring companies, allocating R&D budgets, or launching new business models. Quantified, accurate, and deep intelligence reduces risk.
Strategic analysis requires the market, competitor, technology, and consumer intelligence synthesis into informed perspectives. This allows more calculated responses to opportunities, challenges, and disruption. The high risks of the current environment raise the strategic value derived from intelligence insights.
The quickening marketplace requires decision-makers to arm themselves with intelligence to navigate rising uncertainty and complexity. The solutions and recommendations that flow from analysis keep companies ahead of disruption.
Best Practices for Leveraging Competitive Intelligence
| Dimension | Best Practices |
|---|---|
| People | – Train employees at all levels on applying CI insights – Create cross-functional CI teams – Crowdsource intelligence from frontline employees |
| Processes | – Integrate CI into core planning and decisions – Set key intelligence requirements for each business unit – Hold regular CI strategy meetings with leadership |
| Technology | – Prioritize automation of repetitive tasks – Develop CI dashboards and alerts tailored to different roles – Leverage analytics to uncover insights from data |
Integrate CI into Core Decision-Making Processes
For maximum impact, competitive intelligence should directly inform business strategies and department decisions. Essential best practices include:
- Hold regular CI strategy meetings with executive leadership to discuss the latest findings, trends, and strategic insights.
- Create cross-functional CI teams with representatives from business units like marketing, product, sales, and R&D.
- Develop CI reports, dashboards, and alerts tailored for different business functions based on their decision needs.
- Work with department heads to outline essential intelligence requirements for planning and processes.
- Train employees, from analysts to executives, on applying CI findings through recommendations, scenarios, wargaming, and other framing techniques.
Embedding CI into workflows and conversations becomes a driver of actions rather than an isolated activity. CI informs business plans, marketing campaigns, roadmaps, and mitigation strategies.
Keep an Eye on The Landscape
CI analysts act as the eyes and ears, monitoring the outside forces shaping competitiveness. Key focus areas include:
- Competitors – New products, pricing, promotions, partnerships, acquisitions, and strategies.
- Customers – Shifting preferences, complaints, adoption rates, churn drivers, and unmet needs.
- Channel partners – Performance benchmarks, market insights, emerging partners.
- Macro forces – Economic trends, technology shifts, regulatory changes, sociocultural forces.
- Startup activity – New entrants, innovations, disruptive business models.
This 360-degree perspective ensures leaders avoid internal fixation and consider the external dynamics influencing the market. A strong understanding of the competitive ecosystem clarifies growth opportunities and threats.
Involve Employees at All Levels
Tapping into employees across the company enhances CI by leveraging their unique insights. Frontline sales and service teams hear competitive chatter firsthand. Engineers keep tabs on emerging substitute technologies. Implementing a CI crowdsourcing program engages the collective knowledge of the organization.
Wrap-Up & Final Thoughts
Competitive intelligence offers indispensable guidance for companies navigating increasingly complex and rapidly evolving business environments. By continuously monitoring the strategic moves of current and emerging competitors, along with tracking wider market forces and trends, organizations can pursue data-driven strategies that anticipate disruption.
Advances in data sources, collection tools, and analytics have made competitive intelligence more comprehensive, sophisticated, and actionable than ever before. To fully exploit CI, companies should tightly integrate it into core planning processes, keep a keen eye on the external environment, and tap into employees’ collective knowledge.
With competitive pressures growing, no company can afford to formulate a strategy and make decisions without intelligence backing. Competitive intelligence is an early warning system revealing threats and opportunities that can determine failure or success in hyper-competitive global markets. Organizations that embrace competitive intelligence research and analysis will maintain consistent strategic advantages over rivals.
FAQ
Competitive intelligence research involves the ethical and legal collection and analysis of information about a company’s competitive environment. This encompasses monitoring competitor activities, strategies, and offerings and analyzing broader market forces, trends, and opportunities.
CI became prominent in the 1980s, initially focusing on collecting print publications and news clips. The 1990s saw the rise of the internet and digital information, expanding the scope of CI. The 2000s introduced CI software systems, CRM, and market research data. Today, CI uses advanced analytics, big data, AI, and specialized tools for comprehensive insights.
The main areas include Market Intelligence (analyzing competitors, customers, suppliers, etc.), Competitor Intelligence (monitoring competitor activities and strategies), M&A Intelligence (researching potential acquisition targets), and Win/Loss Analysis (determining the outcome of deals).
Significant trends include Big Data and Advanced Analytics, Automation, Social Media Monitoring, and Cyber Intelligence. These trends have transformed how CI is conducted, making it more comprehensive and actionable.
The rapid pace of change in industries, globalization, disruptive innovations, and the need for data-driven strategic decisions have made CI indispensable. It helps companies anticipate disruption, remain agile, and make informed decisions.
Companies should integrate CI into core decision-making processes, continuously monitor the external competitive landscape, and involve employees at all levels to gather insights. This ensures that CI informs business plans, marketing campaigns, product roadmaps, and mitigation strategies.
New technologies like big data, AI, and automation have transformed CI. They enable more powerful data gathering, real-time monitoring, and sophisticated analysis, providing deeper insights about competitors and markets.
Social media provides real-time insights into competitors. Analysts can quickly gather information on new product launches, campaigns, and other significant activities by monitoring competitor’s social media. It also helps in assessing consumer perceptions of competitors.
Cyber intelligence has become crucial for protecting IP and strategic data with the rise of cybersecurity threats. It involves monitoring hacker communications and potential threats to prevent leaks and security breaches.
