The future of work is undergoing rapid change as new technologies and trends emerge. Organizations must understand how these developments will transform their workforce and strategies. Extensive research by the McKinsey Global Institute analyzing eight countries reveals critical insights about the future of work.
By 2030, automation and AI may displace many jobs, requiring 1 in 16 workers to switch occupations. This highlights the growing need to reskill employees and cultivate adaptability. While some roles face a decline, others will see rising demand. Sectors like healthcare, education, the green economy, and aging populations are projected to grow.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also accelerated specific trends. Remote work, e-commerce, and digital adoption have surged out of necessity. As the pandemic recedes, these trends will persist, reshaping how organizations operate. Firms must stay agile and ready to embrace future ways of working.
The below model from ISG is the most accurate I have seen replicating the future of work.
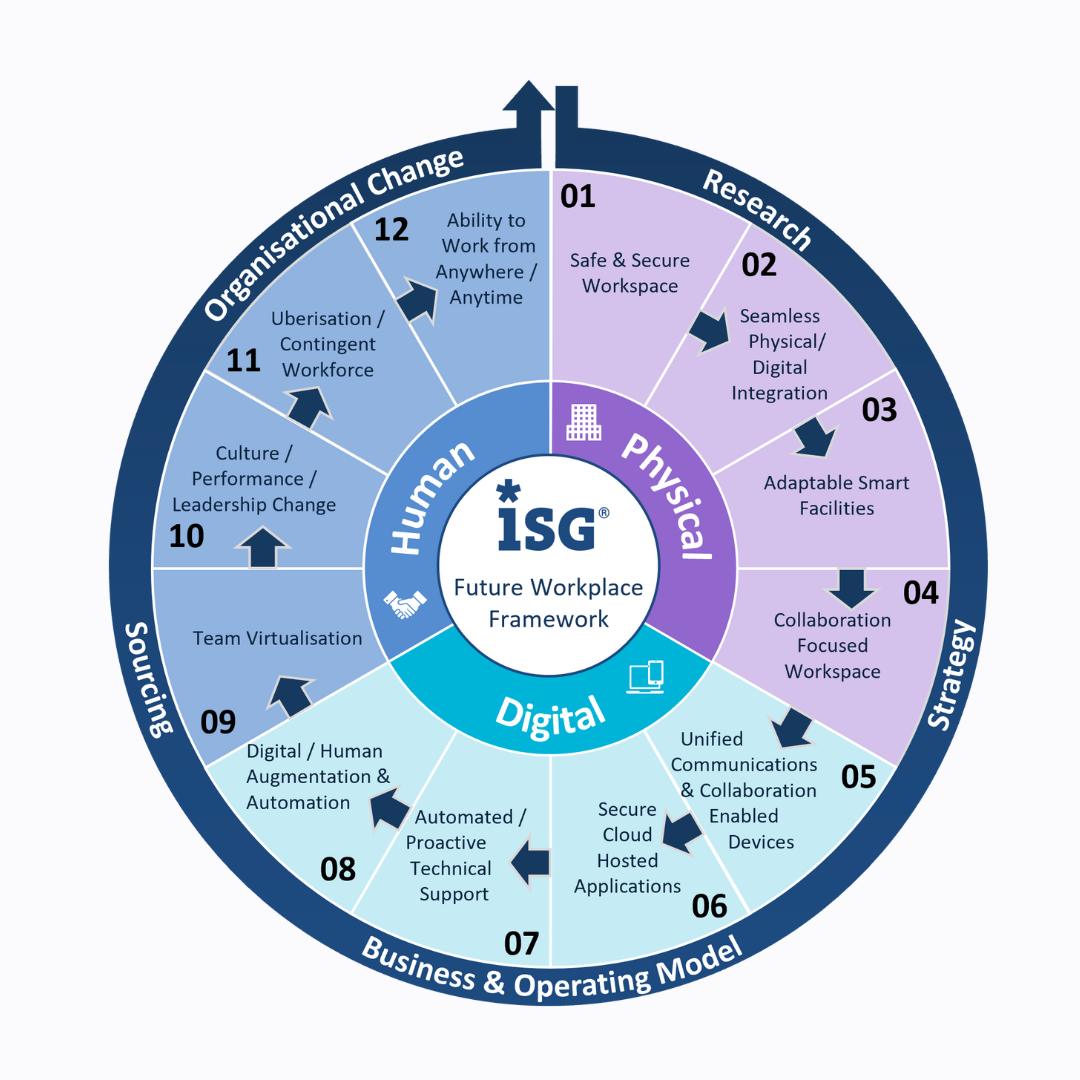
The Future of Remote and Hybrid Work
| Remote Work Trends | Hybrid Work Trends |
|---|---|
| Increasing adoption of remote work policies | Combining on-site and remote work for optimal flexibility |
| Implementation of remote collaboration tools and technologies | Refining operating models to support both on-site and remote work |
| Shift towards outcome-based management and performance measurement | Emphasizing strategic clarity and talent velocity |
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a massive shift to remote work out of necessity. This unexpected disruption has prompted extensive discussions about sustaining remote and hybrid models in the long term. Understanding these trends is crucial for planning as firms navigate this new territory.
Remote work enables business continuity, flexibility, cost savings, and satisfaction. These advantages will drive remote work’s continued growth even after the pandemic wanes. Per McKinsey, 20-25% of workers in advanced economies may be fully remote 3-5 days a week.
Yet, remote work isn’t universally applicable. Jobs requiring on-site tasks or equipment obviously cannot be done remotely. The feasibility depends on the work’s nature, duties, and goals. Hybrid models with on-site and remote work will likely prevail in many organizations.
Adapting to these new models requires focusing on clarity, output-based management, talent development, collaboration, and technology. Organizations can optimize productivity and success with deliberate strategies grounded in trends and data.
Watch this fascinating video for Simon Sinek talking about and defining the future of work.
As organizations plan for the future of work, grasping the trends and nuances of remote and hybrid models is crucial. Implementing flexible policies strategically allows firms to build adaptable and engaging work environments. This approach caters to employee needs for flexibility while maintaining productivity and strategic alignment to drive business success. Thoughtful leveraging of remote and hybrid frameworks will enable organizations to access talent globally, reduce costs, spur innovation, and remain competitive. Companies can optimize these models with deliberate effort and focus to benefit their people and performance.
The Three Core Elements Shaping the Future of Work
Organizations must examine three interconnected elements to strategize for the future: the evolving nature of work, the workforce of tomorrow, and the future workplace.
Understanding the changing nature of work involves analyzing how companies deliver value and accomplish tasks. This knowledge allows firms to align operations with strategic vision. By studying trends in business models, technologies, and market dynamics, organizations can identify risks, capitalize on opportunities, and remain competitive.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| The Nature of Work | Understanding how organizations make money and aligning work with strategic priorities. |
| The Workforce of the Future | Assessing skills and talent needed for future jobs and developing strategies to address talent gaps. |
| The Workplace of the Future | Embracing flexible work arrangements and leveraging technology for virtual collaboration. |
Preparing the future workforce requires assessing current skills gaps and talent needs. As automation increases and digital capabilities become mandatory, reskilling and lifelong learning will be imperative. Firms must implement development programs, promote diversity and inclusion, and foster cultures of continuous growth. Adapting to the evolving expectations of employees will also be critical.
Finally, the workplace of the future transcends physical space. Remote work arrangements, virtual collaboration, and flexible policies are critical to supporting productivity. Organizations must provide technologies, reimagine office design, and measure performance to enable flexibility.
Together, these three elements provide a comprehensive view of the forces driving the future of work. Examining them holistically allows companies to make strategic plans.
The Evolving Nature of Work
The nature of work is shifting as new technologies emerge and customer needs change. To remain competitive, firms must reevaluate business models and processes. Opportunities exist to optimize operations with automation, Artificial Intelligence, and data analytics. Cross-functional collaboration and cultures of innovation are essential to capitalize on new trends.
Organizations must analyze where disruption will likely occur in their industries and take proactive steps to adapt. This may require redefining roles, forming partnerships, and developing new offerings. By continuously improving how work gets accomplished, companies can align operations to strategic objectives.
Preparing the Workforce of the Future
Tomorrow’s workforce must be digitally literate, comfortable with change, and focused on continuous development. Assessing current skills and future needs is crucial to identifying gaps. Organizations must provide resources for reskilling and professional growth.
Building inclusive and diverse cultures will also be key to accessing the top talent globally. With increasing automation, human employees will focus more on creative thinking, strategy, and emotional intelligence. Adapting policies to provide scheduling flexibility and remote opportunities will allow companies to attract skilled talent.
The next generation of workers, Gen Z and Gen Alpha will have different expectations and preferences around work. Having grown up as digital natives, they are highly skilled with technology and expect high connectivity. The latest tools and technologies will be key to engaging and empowering these workers.
Gen Z also highly values flexibility, creativity, and meaningful work. They expect to have opportunities for continuous learning and development on the job. Providing training programs and growth opportunities tailored to their strengths will maximize their retention.
See this video from CNBC about how Gen Z is reshaping the future of work.
Meanwhile, Gen Alpha are true digital integrators who thrive when using technology to express their creativity. Allowing them to leverage their skills through virtual collaboration and digital delivery of work will optimize engagement. Crafting policies with these generations’ preferences will help attract and develop strong talent.
Envisioning New Workplace Models
Advances in technologies enable work to occur anytime, anywhere. The future workplace must provide tools for virtual collaborations and seamless remote work. Rethinking office design to include informal spaces for socializing can foster creativity and connections between on-site and remote workers.
Outcomes should be measured rather than time spent at desks for performance management. Providing the right digital infrastructure will optimize user experience regardless of location. The workplace can facilitate innovation with deliberate strategies to support collaboration and productivity.
Flexible, digitally-enabled models allow organizations to access talent globally and reduce costs. Companies can gain a competitive advantage by embracing virtual capabilities and remote policies.
HR’s Pivotal Role in Shaping the Future of Work
HR professionals play a critical part in preparing organizations for the workforce of tomorrow. Adapting to emerging trends is essential to transforming HR through digitization and agile strategies. By leveraging technology and flexible policies, HR can optimize operations while empowering employees.
Automating administrative tasks enables HR to focus on strategic priorities like skills analysis and development programs. Digital tools also allow faster recruiting and data-driven decision-making through analytics. Embracing agile frameworks further will enable firms to rapidly respond to market shifts and spur innovation.
| HR Transformation | Digitization of HR | Agile HR |
|---|---|---|
| Automating processes | Streamlining recruitment | Flexible work models |
| Leveraging employee data | Analyzing workforce trends | Empowering employees |
| Strategic decision-making | Enhancing employee experience | Promoting collaboration |
HR should advise leadership on talent strategies to access skilled workers globally as the future unfolds. Conducting skills gap analysis and implementing retraining programs will be key to developing talent that meets future needs.
Additionally, HR must focus on optimizing the employee experience through the entire lifecycle. Building inclusive cultures, streamlining onboarding, and promoting belonging can enhance retention and productivity.
HR plays a multifaceted role in driving organizational success amidst the changing nature of work. Digitizing processes, adopting agility, and realigning priorities allow HR to obtain and develop the talent that organizations need to thrive in the modern era. By leveraging technology and human capabilities, HR can lead companies into the future.
Driving Transformation Through Digital HR
HR teams can leverage digital technologies to automate repetitive administrative tasks like payroll processing and benefits management. Relieving HR professionals of these manual constraints enables greater focus on strategic priorities. Advanced analytics provide data-driven guidance for recruitment, learning investments, and long-term planning. Streamlined workflows also create efficient, seamless experiences for employees and hiring managers.
Innovations like AI and machine learning further optimize HR processes. Intelligent algorithms can rapidly parse through high volumes of resumes and profiles to surface optimal job candidates for open roles. Ongoing engagement and performance data aggregation empower HR leaders to make evidence-based decisions on talent initiatives.
Overall, digitization equips HR with expanded capabilities and insight while removing bottlenecks. Instant access to integrated information allows HR groups to operate with agility and scale across global organizations. The transformative power of digital HR tools and philosophies cannot be understated.
Implementing Agile HR Strategies
Agile frameworks in HR champion collaboration, flexibility, and employee empowerment. This allows organizations to respond to external shifts nimbly, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and accelerate innovation.
Autonomous, cross-functional teams foster creative problem-solving. Regular feedback loops and goal alignment further enhance speed and productivity. Onboarding and training should promote adaptability, upskilling, and growth mindsets.
HR is pivotal in cultivating a culture of continuous learning and improvement. With agile strategies, HR enables organizations to organize talent and operations in adaptable ways that meet evolving needs. This empowers resilient and motivated workforces equipped to thrive in times of uncertainty.
The Dual Impact of Automation and Technology on the Future of Work
Automation and emerging technologies are having a transformative effect on the world of work. While bringing immense opportunity, they also create new challenges surrounding job displacement and the need for workforce development.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption of innovations like automation, artificial intelligence, and digital platforms. Their capacity to drive efficiency and resilience has led to rapid integration across sectors. For example, automated warehouses, virtual call centers, and intelligent factories demonstrate these technologies’ potential.
However, as machines increasingly handle routine tasks, human employees need more advanced technical abilities. Working collaboratively with AI systems, creative thinking and adaptability become critical. This growing skills gap means organizations must invest heavily in reskilling and upskilling their people.
Targeted training and development opportunities will enable workers to complement automation rather than compete. Lifelong learning systems and cultures must also emerge to help employees evolve with technology. Proactive workforce preparation can maximize the promise of emerging innovations while minimizing displacement.
With deliberate effort, the rise of automation can augment human strengths rather than replace them. While transitioning to more integrated technologies involves growing pains, the long-term result is smarter, more empowered workers and organizations. Companies that leverage automation strategically and support their people through upskilling will gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
The Promises and Challenges of Automation
Automating repetitive, dangerous, or low value-added tasks promises improved efficiency and safety. Algorithms and robots can operate 24/7, reducing errors and costs. This allows human employees to focus on more strategic priorities.
However, concerns exist about displacing workers in automatable routine roles. Transitioning displaced employees to new functions requires substantial investment in reskilling and development. Organizations must create programs to help workers learn the technical and interpersonal skills needed for future roles.
The pace of automation also demands cultures of lifelong learning. As technologies evolve continuously, merely reskilling once will not suffice. Workers must be empowered to adapt through constant exposure to new tools. A growth mindset throughout the organization is critical.
Preparing the Workforce to Thrive Alongside Technology
To fully leverage automation’s potential, strategic workforce development is required. Training programs should develop digital fluency, creative thinking, and collaboration talent. Curating learning pathways that align with an individual’s strengths and interests will optimize engagement.
Change management processes must also support employees through upskilling. Transparency around automation plans and clear communication are key to easing uncertainty.
Automation and technology are driving significant changes in the future of work. While they can improve efficiency and productivity, they also raise concerns about job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling.
With proactive preparation, organizations can tackle skills gaps created by automation, ensuring technologies complement human employees. A digitally literate, adaptable workforce is critical to gaining the most value from innovations.
Examining the Expanding Role of AI in the Workplace
Artificial intelligence is becoming deeply integrated into the modern workplace, bringing opportunities and ethical dilemmas. AI systems can rapidly analyze data to optimize decisions, workflows, and experiences. Virtual assistants, chatbots, and machine learning algorithms demonstrate AI’s potential to enhance productivity.
However, the expansion of AI also raises valid concerns about perpetuating biases and unfairness if not developed responsibly. Organizations must prioritize ethical AI practices, conducting ongoing audits and monitoring while prioritizing diverse perspectives. With deliberate effort, firms can maximize AI’s promise while proactively addressing its risks.
As AI takes on a greater role, reimagining processes, structures, and employee responsibilities is required for successful integration. The future of work depends on digital transformation that looks beyond just adopting tools. Cultivating agility, learning, and collaboration will allow human and AI capabilities to complement each other.
AI can process volumes of data far faster than humans, identifying data-driven insights and trends that optimize decision-making. It can also handle repetitive administrative tasks, freeing employees’ time for higher-value work. Intelligent algorithms help predict emerging needs and customize experiences.
AI augments workers’ abilities to spot patterns, generate ideas, and refine strategies. It empowers more evidence-based, strategic contributions across all levels. Integrated thoughtfully, AI becomes an asset rather than a threat.
However, to mitigate risk, ethics frameworks and controls must shape AI’s development and use. Ongoing evaluation of its impacts and meaningful diversity in creation are critical.
Driving Transformation Through Digital Fluency
Organizations must focus on digital fluency and agile cultures to fully leverage AI and other emerging capabilities. Training programs should develop adaptability, creative thinking, and collaboration skills. More modular, cross-functional structures allow faster reconfiguration to meet changing needs.
Experimenting and iterating quickly becomes vital to accelerating innovation. Providing access to cutting-edge technologies for pilots empowers bold ideas. The willingness to take calculated risks is essential.
With humans and AI systems closely aligned and augmented by agile, digitally savvy cultures, organizations can continuously enhance performance. Digital transformation requires a holistic paradigm shift beyond just adopting new tools.
| Benefits of Automation and Technology | Challenges of Automation and Technology |
|---|---|
| Improved efficiency and productivity | Job displacement and the need for reskilling |
| Enhanced data analysis and decision-making | Potential for bias and discrimination in AI |
| Streamlined operations and workflows | Cultural shift and change management |
| Opportunities for innovation and growth | Organizational resistance to change |
Optimizing Remote Collaboration in the Future of Work
As remote and hybrid models become more prevalent, enabling seamless collaboration regardless of location is critical. True collaboration requires equal participation and access for all team members, on-site or remote. Organizations must adapt strategies and technologies to foster effective virtual teamwork.
Remote collaboration hinges on providing the necessary tools and resources equitably. Platforms facilitating video conferencing, screen sharing, and real-time document collaboration are essential for productivity. These tools allow teams to work together in real time, bridging physical distances.
Clear communication practices are also imperative in dispersed environments. Establishing consistent channels via instant messaging, project management systems, and video calls encourages transparency. Regular check-ins and feedback loops keep all contributors aligned and engaged.
Careful attention to inclusivity for remote participants creates collaborative experiences where everyone can add value. While adapting collaboration strategies involves challenges, the future of work depends on virtual and hybrid teamwork. With the right structure, tools, and culture, seamless location coordination is achievable.
Providing Equitable Tools and Channels
Enabling seamless remote collaboration requires giving all contributors access to the same real-time platforms. Standardizing inclusive video conferencing, file sharing, and project management tools allows equal participation. Policies should mandate access parity for remote team members to prevent collaboration barriers.
Informal communication channels like enterprise chat and social forums are important for relationship-building and transparency. While remote workers miss impromptu in-office conversations, digital channels can close these gaps. Occasional in-person meetings, when feasible, further help nurture connections. However, care must also be taken to structure inclusive participation for remote attendees. With the proper tools and policies, geographic distance need not impede effective collaboration.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Video Conferencing | Allows teams to hold virtual meetings, share screens, and collaborate in real-time. |
| Document Collaboration | Enables multiple team members to work on the same document simultaneously, making it easier to collaborate and track changes. |
| Instant Messaging | Facilitates quick and easy communication among team members, allowing for real-time discussions and updates. |
| Project Management Software | Helps teams stay organized, manage tasks, and track progress, fostering collaboration and accountability. |
Fostering an Inclusive Culture
While providing proper tools is crucial, organizations must go further to build inclusive cultures that empower remote participants. Setting expectations like keeping cameras on during meetings and allowing remote attendees to interrupt organically gives virtual team members equal voice and presence. Emphasizing output-driven work policies rather than hours logged builds trust in remote workers and gives them autonomy. Investing in manager training to support effective engagement and development of remote teams is also recommended.
Promoting social connections amongst on-site and remote staff and celebrating shared wins helps foster unity and prevent fragmentation. With concerted efforts towards equitable policies, norms, and training, geographic distance can become a non-issue in collaboration. An intentionally nurtured culture makes remote and on-site workers feel equally valued, included, and able to contribute fully.
Prioritizing Security in the Evolving Work Landscape
Modernizing security is imperative as work trends bring increased flexibility and remote access. Risks like data breaches, hacking, and phishing intensify with more dispersed environments. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity aligned to emerging work models to safeguard information and operations.
Updating network protections through tools like multi-factor authentication, advanced firewalls, and encryption protocols is recommended. Ongoing monitoring via audits helps identify gaps, while training builds employee awareness.
Physical and virtual safeguards must work in tandem – secure facilities, strong access controls, and encryption. Developing holistic strategies to secure data and prevent unauthorized access is key.
Security must remain top of mind in the evolving workplace, where on-site and remote work blend. Mitigating risks through modern policies, infrastructure, and culture building allows organizations to embrace flexibility confidently. Prioritizing multilayered security unlocks the possibilities of emerging work arrangements rather than impeding them.
Adapting Security Frameworks
As remote and hybrid models become more pervasive, legacy security strategies need updating to address new risks. Implementing robust device management, continuous system monitoring, and regular penetration testing helps uncover vulnerabilities in today’s distributed environments.
Deploying multi-factor authentication adds critical identity verification before granting network access. Encrypting endpoints, networks, and sensitive data provides additional protection.
Protocols must also be refreshed to secure both physical and cloud assets seamlessly. In modern workplaces, security frameworks must be as dynamic as the work models to provide adequate safeguards.
Promoting a Culture of Vigilance
Along with technical controls, nurturing a culture of security awareness empowers employees to help protect assets. Providing ongoing education makes staff more alert to phishing attempts and other threats. Encouraging vigilance and requiring strong passwords enhances baseline security hygiene.
Frequent reporting reminds personnel to remain aware of vulnerabilities while recognizing those who flag issues incentivizes participation. Robust technical defenses are most effective with an actively security-conscious organizational culture. Together, these enable a multilayered security posture ready for the future of work’s evolution.
Transforming the Way We Work: Innovations and Challenges
| Innovation | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Automation in the workplace | Streamlined processes, increased productivity, and better allocation of resources |
| Productivity tools | Improved collaboration, efficient task management, and enhanced team productivity |
The future of work brings exciting innovations and daunting challenges that organizations must navigate adeptly. Workplace transformation through new technologies promises enhanced efficiency and productivity but also requires adaptation. By embracing innovations thoughtfully while addressing emerging challenges, companies can optimize for the evolving environment.
Automating repetitive tasks holds tremendous potential to boost efficiency. Streamlining workflows through automation enables employees to focus on more strategic responsibilities that add value. Organizations should explore automation opportunities across departments to unlock productivity gains.
Advanced collaboration and communication tools also facilitate new ways of working. Integrating intuitive productivity platforms empowers seamless teamwork, whether on-site or remote. This enhances workforce connectivity, sparking innovation and creativity.
However, as technology reshapes work, maintaining a work-life balance becomes crucial. The future workplace must enable flexibility and well-being. Organizations should nurture cultures that support employees in achieving harmony between their personal and professional lives.
Reskilling the workforce is critical to addressing skills gaps created by automation and digital disruption. Investing in continuous learning and development opportunities will help employees gain future-proof capabilities. With proactive preparation, companies can maximize innovations in the modern workplace while supporting their people through the transition.
Embracing the Future of Work: Tools and Insights
The future of work brings opportunities and challenges that organizations must navigate adeptly. Businesses must leverage the right technologies and insights to adapt to this transformation successfully. Investing in tools like project management platforms, virtual meeting software, and employee engagement systems can drive efficiency and alignment.
| Data Analytics | Insights & Strategies |
|---|---|
| Project management software | Ensure efficient collaboration, task management, and project tracking |
| Virtual meeting platforms | Facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among remote teams |
| Employee engagement platforms | Promote employee satisfaction, recognition, and development |
| Workforce management software | Optimize talent management, performance, and productivity |
| Data analytics | Gain insights into workforce trends, skill gaps, and employee performance |
Staying updated on the latest trends and innovations is critical for strategy development. Deep knowledge of emerging technologies, workforce dynamics, and customer behaviors allows organizations to meet changing needs proactively. This level of insight can be achieved through continual learning, industry events, and thought leader partnerships.
Unlocking Workforce Management Success
Workforce management is integral for organizations to optimize talent and performance amidst the future of work. Leveraging digital tools and data-driven analytics enhances employee engagement, productivity, and business outcomes. Comprehensive workforce strategies involve acquiring, developing, and retaining top talent, including performance management, succession planning, and continuous learning to cultivate talent.
Workforce management systems can automate routine HR tasks while providing actionable insights. These tools empower efficient resource allocation, skills gap identification, and data-informed talent decisions. By embracing workforce technologies, companies can build adaptive, high-performing teams ready for the future.
The future of work requires organizations to harness the power of technology, data, and insights. By embracing the right tools and strategies, businesses can transform their workforce, enhance collaboration, and drive sustainable growth.
Preparing for the evolving work landscape is a key imperative across industries. Businesses can gain a competitive advantage with the right technologies, data-driven insights, and workforce strategies. Fostering agile, adaptable cultures is also essential for employees to thrive. Organizations proactively embracing the future of work will reap the rewards of stronger talent and performance.
Wrap-Up Thoughts
The future of work is evolving rapidly, transformed by advancements in technology, changing workforce dynamics, and new workplace norms. To stay competitive, organizations must proactively adapt to these developments.
Several key insights can guide strategic planning. Hybrid remote policies will likely endure, requiring updated operating models focused on clarity, output-driven management, talent development, collaboration, and technology integration. Automation and AI bring promise and disruption, necessitating workforce upskilling and digital fluency.
HR plays a pivotal role in this landscape, evolving to provide strategic guidance on reskilling, digital transformation, and optimizing the employee lifecycle. Remote collaboration tools and inclusive culture building are essential to facilitate productive virtual teams. And as work becomes more distributed, robust cybersecurity strategies must be implemented to safeguard assets.
Companies can unlock future possibilities by strategically embracing workplace transformation, strategically leveraging emerging technologies, and supporting worker wellbeing. With proactive preparation, the evolving nature of work can be met with opportunity rather than apprehension. Those organizations that adapt adeptly will gain a competitive advantage and thrive.
The rapid evolution of the work landscape shows that adaptability and continuous learning are now essential skills for every worker. Technological innovations and the pandemic’s impacts have accelerated change, increasing the risk of job displacement. The growing remote and hybrid work discussion highlights the need to blend technology with human-focused policies. Exploring the interdependent dimensions of work’s nature, workforce readiness, and flexible work models provokes meaningful reflection. How can organizations strategically navigate this new dynamic terrain? The path forward must nurture work cultures and policies that engage employees, spark productivity, and build adaptable mindsets.
FAQ
The key trends in the future of work include the growth of high-skill jobs, the decline of middle- and low-skill jobs, the adoption of remote work, the impact of automation and technology, and the focus on skills and talent development.
Remote work is expected to persist even after the pandemic, with around 20 to 25 percent of workforces in advanced economies potentially working from home three to five days a week.
Organizations can prepare for the future of work by understanding the nature of work, assessing the skills and talent needed for future jobs, and embracing advancements in technology and flexible work arrangements.
HR plays a crucial role in shaping the future of work by undergoing transformation, digitizing processes, and becoming a strategic partner to the business. HR’s focus should shift to strategic priorities, talent management, and creating a positive employee experience.
Automation and technology will drive significant changes in the future of work, improving efficiency and productivity. However, they also raise concerns about job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling.
Organizations can facilitate remote collaboration by leveraging tools and technologies, such as virtual meeting platforms and real-time collaboration tools, to enable seamless communication and inclusivity among team members.
Organizations should modernize their security measures, adopt strong cybersecurity practices, and integrate security considerations into future work models to protect data and operations in both physical and virtual environments.
Organizations face challenges such as reskilling and upskilling the workforce, ensuring inclusivity and diversity, and effectively managing the evolving work dynamics brought about by the future of work.
Organizations should invest in future-focused tools like project management software, virtual meeting platforms, and employee engagement platforms. Staying updated on the latest insights and trends in the future of work is also crucial for developing effective strategies.
